Overview
Hepatitis C is inflammation of the liver caused by a virus that disrupts liver function. One of many hepatitis infections, hepatitis C, is believed to be one of the most serious viruses. The hepatitis C virus passes from one individual to the next via contaminated blood. Therefore, many patients contract hepatitis C as a result of sharing hypodermic needles.Symptoms
This viral infection is so dangerous because it usually does not present any signs or symptoms in its early stages. Often the patients are not diagnosed with hepatitis C until other tests reveal significant liver damage. And it can take decades for the liver to show that damage. At that time, patients may experience muscle or joint pain, nausea, poor appetite, fever, fatigue, and yellowing of the skin or eyes, also known as jaundice.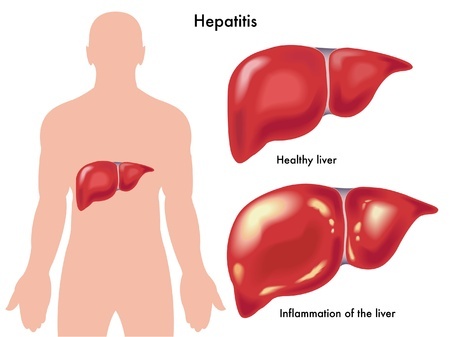
Risk Factors
Coming in contact with objects or surfaces that contain blood other than your own will put you at great risk for contracting hepatitis C. Nevertheless, certain careers or lifestyles can place you in a position that increases your risk of getting hepatitis C. These could be hospitals, tattoo parlors, or anywhere exposed blood is in abundance.Likewise, if you received clotting factor concentrates before 1987, received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992, inject recreational drugs, have human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), or were born to a woman with hepatitis C, your chances are greater of developing hepatitis C. Some other risk factors include getting a body part pierced or tattooed in a non-sterile environment or with non-sterile equipment and receiving hemodialysis treatments for an extended period of time.
Diagnosis
Hepatitis C is often diagnosed with already existing extensive liver damage. Examples of liver damage are scarring, or cirrhosis, of the liver tissue, liver cancer, or complete liver failure. Still, your doctor will ask you a series of questions about your medical history and your family’s medical history to ensure that a hepatitis C diagnosis is the right diagnosis.Your doctor will also perform some blood tests to confirm diagnosis. These tests should reveal if you definitely have the hepatitis C virus, how much of the virus is in your blood, and how the virus functions in your body. He or she may also perform a liver biopsy by inserting a thin needle through your skin and into your liver to remove a small tissue sample for analysis.
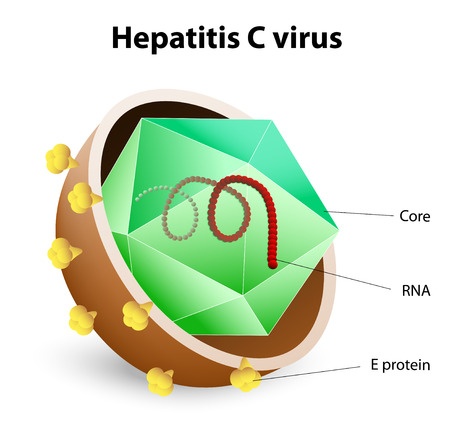
All this information assists your doctor greatly in planning treatment. But, do not be afraid or ashamed to ask your doctor questions about your condition. After all, the more informed you are the more proactive you can be in fighting your hepatitis C infection.
Treatment
In some cases patients do not receive the treatment immediately. Doctors may choose just to schedule you for follow-up blood tests to monitor your liver function. In other cases, your hepatitis C treatment may consist of antiviral medication, vaccinations, or a liver transplant.- Antiviral medication - clears the hepatitis C virus out of your body. Your doctor may prescribe you just one or a combination of antiviral medications that you must take for several weeks. These drugs do have side effects such as flu-like symptoms, fever, fatigue, headache, and depression. If your side effects become too much for you to bear, your doctor may suspend your hepatitis C treatment.
- Vaccinations - can prevent you from contracting the hepatitis A or hepatitis B viruses. Getting either of those viruses while fighting the hepatitis C virus can greatly inhibit treatment and make your liver damage even worse.
- Liver Transplant - may be your most viable option for hepatitis C treatment if your liver is beyond repair and other facets of your health are beginning to decline. Your liver transplant may be an entire liver from a deceased donor or a partial liver from a living donor. Either way, introducing healthy liver tissue to your body while taking antiviral medication can help you overcome the hepatitis C virus.










