Overview
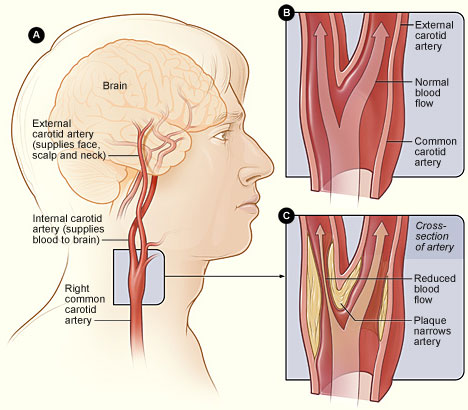
Carotid arteries are a pair of large blood vessels that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood. Carotid artery disease, also known as carotid artery stenosis, is a disease in which the inside space (lumen) of the carotid artery tubular structure is constricted, narrowed or even blocked, usually as a result of atherosclerosis or arteriosclerotic vascular disease.Atherosclerotic plaques (atherosclerotic lesions) are fatty, waxy deposits which form on the inner wall of a blood vessel from various substances transported through the bloodstream, including cholesterol, fat, proteins, inflammatory cells, cell debris, and calcium. The buildup of such plaques in one or both carotid arteries brings about impaired supply of oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the areas of the brain responsible for thought processes, speech, maintaining personality traits, sensory and motor functions.
The dangerous part is that such a buildup develops slowly and is hardly ever noticed by the affected person.
Symptoms
Quite often, especially in its early stages, carotid artery disease does not show any signs or symptoms until it severely narrows or blocks a carotid artery. Signs and symptoms may include a bruit (characteristic whooshing sound detected during stethoscope examination of the arteries), a transient ischemic attack (TIA, mini-stroke), or a full-scale stroke. Not all people who have carotid artery disease have bruits. TIA is truly one of the crucial warning signs of a stroke. It occurs when a blood clot temporarily blocks carotid artery and thus abruptly halts blood supply to the brain. Signs and symptoms of a stroke or TIA may include:- Sudden numbness or weakness in the face or limbs, often on only one side of the body
- Trouble speaking and understanding speech
- Sudden loss of vision or blurred vision in one or both eyes
- Difficulty swallowing
- Dizziness or confusion
- Loss of balance and coordination
- A sudden, severe headache with no known cause
Risk Factors
Factors that impose stress to the arteries and increase the risk of injury, buildup of atherosclerotic plaques and in general are linked to the development of atherosclerosis increase the risk of carotid artery disease. They include a family history of atherosclerosis or coronary artery disease, high blood pressure (hypertension), obesity accompanied by sedentary lifestyle, diabetes, abnormal blood-fat levels, smoking, physical inactivity and age.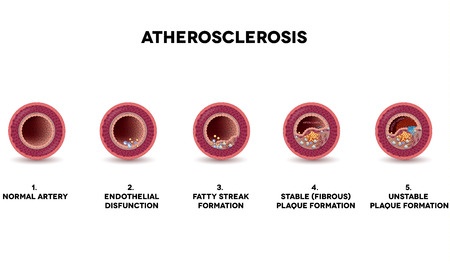
Diagnosis
First of all, regular medical examinations and a thoroughly medical history that records risk factors and any signs or symptoms related to this condition may facilitate the early detection of the disease. While examining carotid arteries with a stethoscope, doctor may detect a bruit resulting from altered blood flow in the artery. To find out more, your doctor may request certain tests which allow assessing the blood flow and pressure, as well as possible narrowing of the blood vessel. Carotid duplex ultrasound is one of the common, noninvasive tests used to check for carotid artery disease. Carotid angiography is an invasive imaging procedure employing special contrast dye injected with a catheter that is been threaded directly into carotid arteries. The technique allows obtaining and analyzing the detailed X-ray images.
Computerized tomography angiography (CTA) is an imaging test that uses advanced computerized tomography (CT) technology, along with intravenous contrast dye, to obtain high-resolution, 3D images of the carotid arteries. Magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) is a specialized type of magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to provide images of the carotid arteries. In many instances, MRA procedure can provide information that cannot be obtained from an X-ray, ultrasound, or computed tomography (CT) scan. This imaging test can provide important information about the condition of carotid and vertebral arteries and the degree of the stenosis.
Treatment of Carotid artery disease
The main goal in treating the carotid artery disease is the prevention of stroke. Overall, the treatment includes lifestyle modifications and management of chronic conditions such as hypertension and high levels of lipids in the blood with the help of prescribed medications and medical procedures.Life Style
Life style change include getting the appropriate level of physical activity, reducing the stress level, losing weight, quitting smoking, eating healthy foods and reducing the amount of consumed salt. Managing of chronic conditions implies controlling the blood pressure and maintaining the healthy level of cholesterol and other lipids in the blood.Medications
Certain medications may also be used under the doctor’s supervision to control the chronic conditions and prevent the blood clots from forming. Daily aspirin or some other blood-thinning agents may be prescribed. Doctor may recommend taking certain medications to control blood pressure, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (Enalapril), Angiotensin II receptor antagonists (Losartan) or calcium channel blockers (Amlodipine), or/and a statin medication (Simvastatin) to lower the blood level of cholesterol.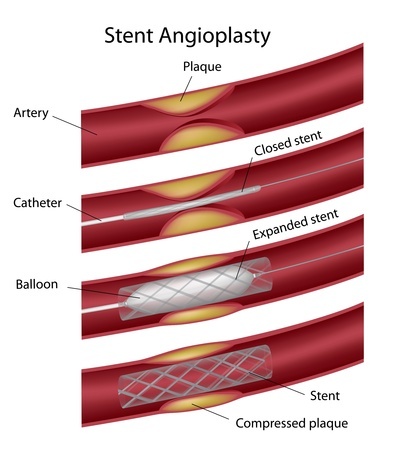
Endarterectomy and Angioplasty
In the case of severe narrowing or blockage in the carotid artery, a special procedure may be required to open the artery and improve blood flow to the brain, and thus to prevent a future stroke. Currently two major procedures are used:- Carotid endarterectomy is surgical procedure and the most common treatment for severe cases of carotid artery disease. The plaque is removed through an incision and then repaired with either stitches or a graft.
- Carotid angioplasty and stenting is applicable for some patients when carotid endarterectomy is contraindicated. During this procedure a tiny balloon is delivered by catheter to the site where carotid artery is severely narrowed or blocked. The balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and a stent (a small wire mesh cylinder) is implanted to keep the artery from narrowing and blocking again.










