Intoduction
When you have knee problems, even simple movements can bring debilitating pain. Arthritis can cause severe damage to the knee joint, making climbing stairs, riding a bike or even walking extremely difficult or impossible. For people with severe knee damage, a knee replacement, also called knee arthroplasty, may be the best solution. Learn more about knee replacements in this guide, including risk factors and what to expect during recovery.
Who Should Consider Knee Replacement
Knee replacements are usually performed for people age 50 or older who have severe arthritis in the knee joint. This is usually caused by rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative arthritis. The arthritis slowly wears away at the bones, causing intense pain and severely limited range of movement.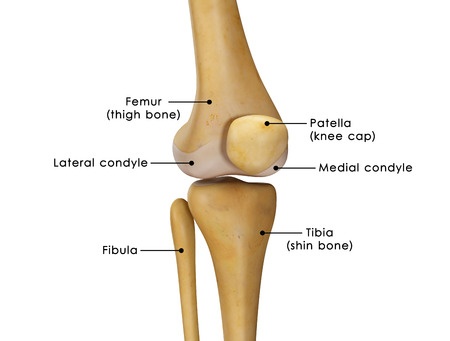
Unlike with a broken kneecap or other acute bone problem, arthritis in the knee causes chronic pain that gets worse as the condition progresses. Physical activities such as walking, jogging, or even sitting and standing back up are exceedingly painful. If you suffer from debilitating arthritis in the knee, it may be time to consider a total knee replacement. Talk with your doctor about getting an appointment with an orthopedic surgeon, who can assess your knee joint and discuss whether a knee replacement is right for you.
The Knee Replacement Procedure
Knee replacements are performed by an orthopedic surgeon. Before your surgery, your surgical team will talk with you to help decide whether to use a spinal anesthesia, where you will be awake but have no sensation from the waist down, or general anesthesia, which renders you unconscious during the procedure.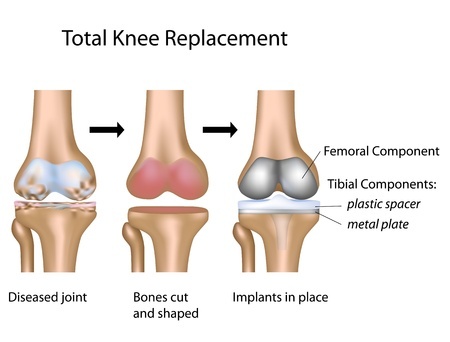
During the operation, your knee remains bent so that all the surfaces of the knee joint are fully visible. The surgeon will carefully make an incision about 6 to 10 inches (15 to 25 centimeters) long, then move your kneecap aside and cut away the damaged surfaces.
Once the joint surfaces are ready, the surgeon inserts the pieces of the artificial joint and attaches them. Before the incision is closed, he or she will bend and rotate your knee, balancing it to make sure that it functions correctly. Knee replacement surgery usually takes about two hours.
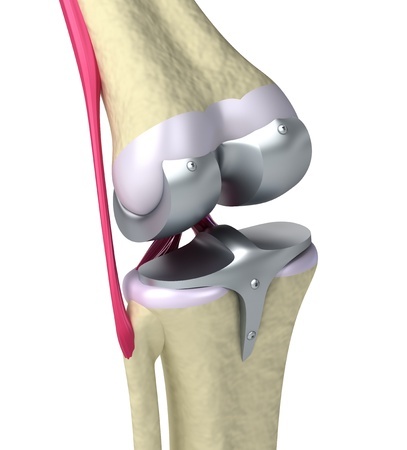
Artificial joints for the knee are made from high-quality plastic or surgical metal, such as steel or titanium. Your orthopedic surgeon will discuss the different knee joints with you before the surgery and recommend what would work best for you based on factors such as your activity level. Artificial knee joints are custom-designed so that your knee replacement is the proper fit for your body.
Aftercare
After your knee replacement, you will be in recovery for an hour or two and then transferred to your room. The typical length of a hospital stay is two or three days. During your hospitalization, you should move your foot and ankle to increase blood flow to your leg muscles. This will help prevent swelling and blood clots. You may also be given blood thinners and compression socks to further decrease the risk.The day after your surgery, you will begin physical therapy. Your physical therapist will show you how to exercise your knee. You are more likely to have a good recovery if you follow your surgeon’s instructions regarding exercise and wound care. Physical therapy will include a graduated walking program and knee-strengthening exercises.









